HYMOD-KZ database and deficit areas
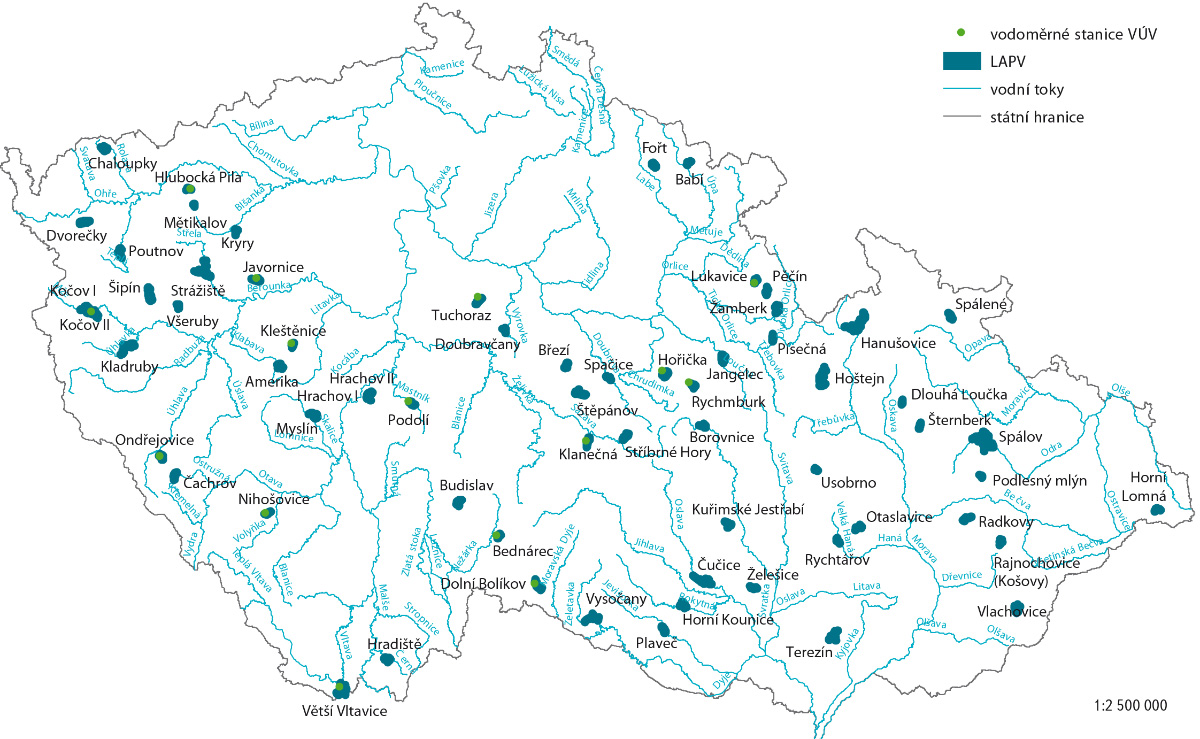
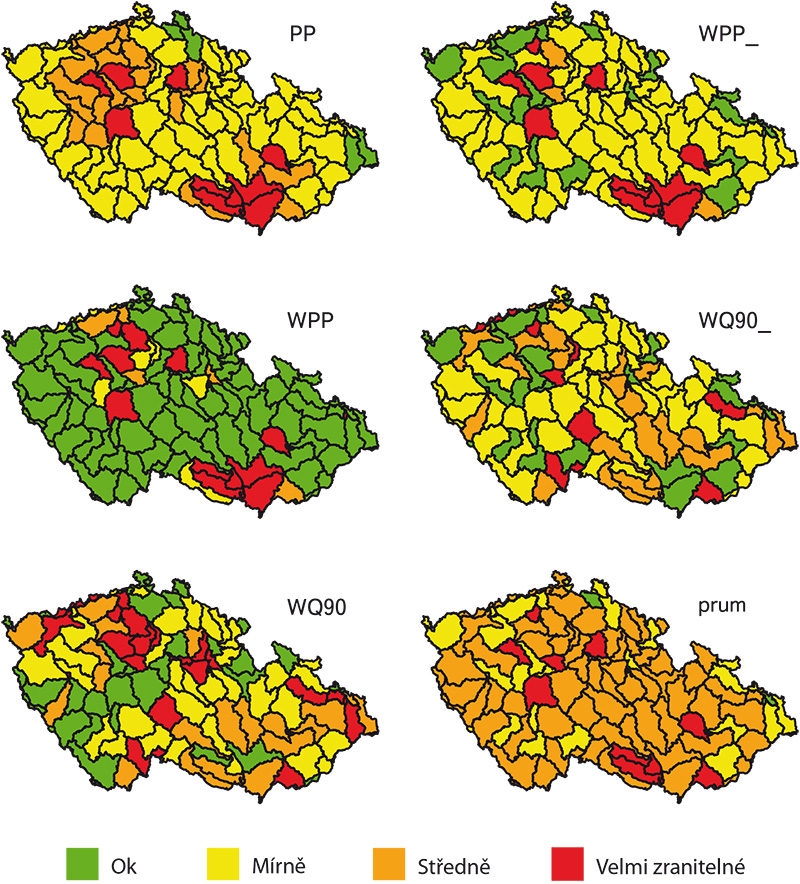
This article describes the HYMOD-KZ database, available at https://shiny.vuv.cz/HYMOD-KZ/. The database provides detailed results of hydrological modelling and hydrological balance analysis of catchments (water bodies) for current and future climate conditions; it also includes updated deficit areas, the description of which is part of this article. This tool can serve as a foundation for water management ex-perts, academia, and the broader professional community as it provides outputs at the spatial resolution of water bodies. The graphical rep-resentation of results facilitates understanding of complex hydrological phenomena and supports decision-making in water management planning.