This article is available in Czech only. For translation or more information on this topic, please contact author.
SOUHRN
Výzkum biofilmů probíhá v rámci projektu „Posílení a ochrana populace perlorodky říční v NP Šumava“ již od roku 2018, kdy byly hledány a testovány vhodné výzkumné metody a postupy studia vývoje biofilmů na hyporheických sedimentech (např. inkubace skleněných kuliček versus inkubace říčního sedimentu, granulometrický průzkum sedimentů dna) a vybrány nejvhodnější lokality pro umístění experimentálních zařízení. V roce 2019 byl proveden na třech vybraných lokalitách testovací tříměsíční výzkum hyporheických biofilmů v toku Vltavy v NP Šumava s ohledem na juvenilní perlorodky, jejich potravní nároky a dostatečné nasycení intersticiální vody kyslíkem. Cílem tohoto výzkumu bylo jak ověření zvolených metod a účinnosti experimentálních zařízení pro sledování vývoje a kvantifikaci hyporheického biofilmu narůstajícího na inkubovaném říčním sedimentu za určitý čas, tak i sledování obsahu a koncentrace kyslíku rozpuštěného v intersticiální vodě a jeho změny ve vztahu k narůstající biomase hyporheického biofilmu.
Tento příspěvek se věnuje výzkumu hyporheických biofilmů řeky Vltavy v NP Šumava, který v návaznosti na zkušební výzkum v roce 2019 probíhal na stejných lokalitách od dubna do listopadu roku 2020. Výsledky analýz a měření poskytují odpovídající hodnoty kyslíku, teploty i biomasy biofilmu typické pro podhorský tok oligotrofního charakteru v chráněném území. Nasycení intersticiální vody kyslíkem je po většinu roku pro perlorodku říční dostačující, výjimku tvoří letní období, kdy na sledovaných lokalitách došlo k náhlým poklesům koncentrace, pro které zatím nemáme uspokojivé vysvětlení. Detekce polysacharidů jakožto proxy pro mikrobiální biofilm společně s naměřenými hodnotami celkového organického uhlíku (TOC) na inkubovaném sedimentu naznačují dostatečnou potravní základnu pro juvenilní perlorodky obývající intersticiální hyporheické prostředí Vltavy.
Kompletní vyhodnocení našeho sledování bude provedeno po ukončení výzkumu, který probíhá i v letošním roce 2021, a poskytne nám možnost porovnat data mezi sebou v průběhu dvou let.
ÚVOD
Perlorodka říční (Margaritifera margaritifera) je kriticky ohroženým druhem mlže s velmi složitým životním cyklem. Po larvální parazitické fázi na žábrách rybího hostitele a po procesu metamorfózy následuje vývoj juvenilní perlorodky v říčních sedimentech toku (tzv. hyporheická zóna). Toto období je považováno za jednu z nejkritičtějších fází jejího života [3], především v důsledku degradace těchto stanovišť znečištěním a následnou kolmatací [2], ale také v důsledku vývoje filtračního aparátu u těchto mladých perlorodek [3]. Mladé perlorodky zahrabané v hyporheickém sedimentu po dobu 5 až 10 let se tak mohou potýkat s nedostatečným nasycením intersticiální vody kyslíkem, ale i s nevhodnou skladbou potravy – detritu [1]. U perlorodky říční dochází během prvních 44 měsíců života k žaberní ontogenezi, která se odvíjí více od velikosti jedince než od jeho stáří. Až od velikosti 4–5 mm dochází u juvenilní perlorodky ke zvýšení počtu žaberních oblouků natolik, že je schopna efektivní filtrace. U jedinců menších sice dochází k postupné přestavbě a vývoji žaberních oblouků, ale ty ještě nejsou schopny filtrovat potravní částice z vody tak jako u dospělých jedinců (cilie nemají patřičnou hustotu). Mladé perlorodky (do 4–5 mm) si tak získávají potravu sběrem částic pomocí svalnaté nohy porostlé ciliemi [2, 3]. Z tohoto hlediska je pro mladé jedince, hledající si potravu stíráním hyporheických sedimentů, velmi důležitá permeabilita dnových sedimentů [1, 4]. Jako jedna z možností potravy pro juvenilní perlorodky vyvíjející se v říčních sedimentech se jeví hyporheický biofilm [5].
Hyporheál je druh habitatu, který je shora ohraničen vodou povrchovou a ze spodní strany vodou podzemní [9]. Jedná se o označení dnových sedimentů, které prostřednictvím pórů umožňují komunikaci vody říční s vodou podzemní [6]. K této komunikaci dochází v důsledku rozdílných tlakových zón, kdy se povrchová voda zanořuje do hyporheálu a my hovoříme o tzv. downwel- ling zóně. Tam, kde je z hloubky intersticiální voda vytlačována směrem k povrchu, hovoříme o upwelling zóně [9]. Hyporheická zóna slouží nejen jako refugium pro řadu vodních organismů [6], ale hraje také velmi důležitou roli v říčním metabolismu a koloběhu živin, jež jsou prostřednictvím hyporheického společenstva mikroorganismů zpřístupněny dalším konzumentům [6, 7]. Jednotlivá zrna hyporheického sedimentu jsou, stejně jako mrtvá rostlinná a živočišná hmota, pokryta biofilmem – společenstvem bakterií, archeí a hub spojených extracelulární polymerní matricí [8, 9]. Hyporheické biofilmy pokrývající sedimenty řek jsou označovány jako „mikrobiální kůže“ [8], která svou adsorpcí, retencí a transformací živin a látek významně ovlivňuje biogeochemické toky živin. Mezi nejdůležitější procesy, kterých se říční biofilmy účastní, patří koloběh uhlíku prostřednictvím degradace a transformace organického materiálu (OM) [7, 8]. Říční biofilmy slouží jako úložiště rozpuštěného organického uhlíku (DOC) a jejich činnost v přeměně rozpuštěného organického materiálu (DOM) na partikulovaný organický materiál (POM) je mimo jiné jedním z hlavních procesů v říčním samočištění [10].
Stěžejním cílem tohoto výzkumu je prokázat přítomnost mikrobiálních biofilmů na inkubovaných sedimentech. Jako indikátor přítomnosti biofilmu (tzv. proxy) byly zvoleny polysacharidy, které tvoří základní strukturní jednotky tzv. extracelulární polysacharidové matrice biofilmů. Dalším z cílů pak bylo zjistit, zda rozvoj biofilmů a akumulace organických látek v intersticiálních sedimentech mohou nějakým způsobem ovlivnit hodnoty rozpuštěného kyslíku v intersticiální vodě sedimentů, jehož koncentrace je kritická pro přežívání juvenilních perlorodek.
Materiál a metodika
Lokality
Pro umístění experimentálních zařízení byly záměrně vybrány tři odlišné lokality řeky Vltavy v NP Šumava (obr. 1). Výzkumné místo nacházející se na Teplé Vltavě, charakteristické standardním štěrkopískovým dnem je pro naše účely označeno jako Dobrá na Šumavě (48.8805625N, 13.8686922E). Ovesná (48.8258247N, 13.9356317E) leží pod soutokem Teplé a Studené Vltavy a je typická štěrkopískovým dnem, ve kterém je větší zastoupení písku. Poslední místo pro výzkum bylo zvoleno na Studené Vltavě (48.8632139N, 13.8630597E). Jedná se o pravostranný přítok Teplé Vltavy, jehož charakter dna odpovídá štěrkopísku s velkými kameny. Všechny toky leží v oblasti vyšší než 700 m n. m.
Obr. 1. Charakter sedimentů dna na lokalitách Dobrá na Šumavě, Ovesná a Studená Vltava (zleva)
Fig. 1. Character of bottom sediments at Dobrá na Šumavě, Ovesná a Studená Vltava (from left)
Experimentální zařízení
Krabice
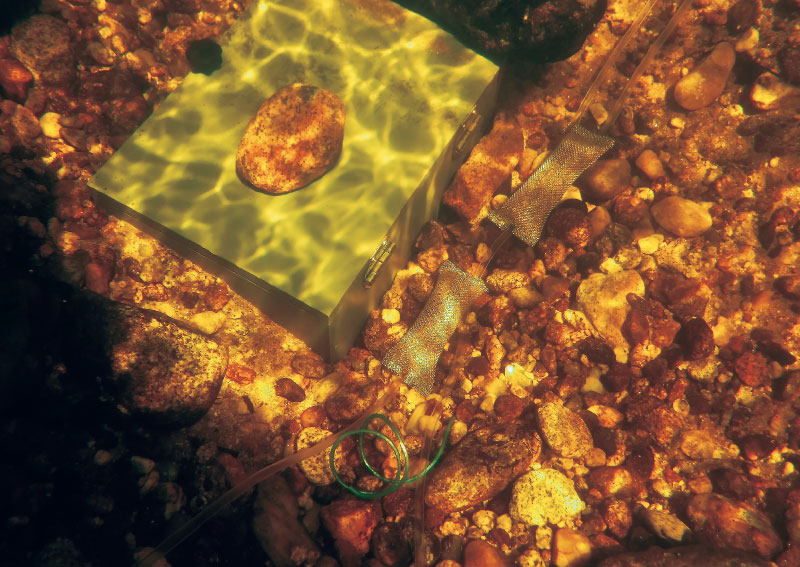
Původní model experimentální krabice byl vytvořen Puschem pro výzkum respirace společenstva hyporheických sedimentů, prostorové distribuce heterotrofní aktivity v sedimentech (krabice umožňovala výzkum biomasy biofilmu až do hloubky 40 cm) a jejího propojení s hydraulickými vlastnostmi toku [11]. Krabice velmi dobře splňuje požadavky pro růst biofilmu či akumulaci látek v různých hloubkách hyporheické zóny. Pro náš výzkum byly dle původního modelu, ve spolupráci s Martinem Rulíkem, vyrobeny tři krabice poloviční velikosti. Uvnitř krabic jsou ve stojanu, horizontálně v hloubkách 10 a 20 cm, umístěny dva válce o objemu 500 ml, jejichž konce jsou uzavřeny víčky se síťovinou o velikosti ok 1 mm. Válce umožňují výzkum biomasy biofilmu ve vertikálním profilu dna řeky. Samotná krabice exponovaná ve dně je stabilní a umožňuje snadné vyjmutí (či navrácení) vnitřního stojanu s válci se zachováním polohy krabice ve dně (obr. 2). Po vyjmutí je možné válce napojit na oxymetr a před dalšími analýzami změřit respiraci intaktního biofilmu in situ.
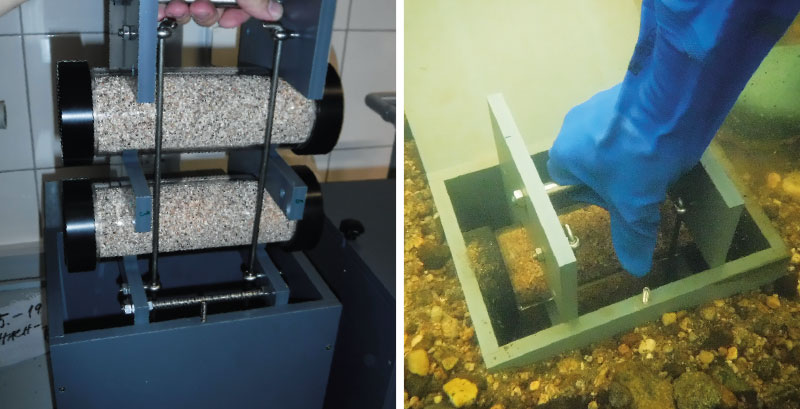

Obr. 2. Experimentální krabice
Fig. 2. Experimental box
Válečky
Pro zachycení variability v plošném nárůstu biomasy hyporheického biofilmu a zkoumání jeho vlivu na obsah kyslíku v intersticiální vodě válečků těsně pod povrchem dna (z důvodu dostatečného nasycení intersticiální vody kyslíkem je dle Simona [1] považována za maximální možnou hloubku výskytu juvenilů v hyporheálu hloubka 10 cm) byly vyrobeny experimentální válečky z nerezové síťoviny o délce 10 cm (obr. 3). Dovnitř válečků je zavedena silikonová hadička k jímání intersticiální vody a měření kyslíku in situ během inkubace válečků 3–5 cm pod povrchem dna. Voda je za pomoci injekční stříkačky nasávána nad hladinu říční vody z metr dlouhé silikonové hadičky ústící dovnitř válečku. Tato hadička byla na dolním konci ve válečku zakončena dvěma vrstvami tkaniny uhelon o velikosti ok 40 µm (vnitřní vrstva) a 100 µm (vnější vrstva), aby do ní nebyl nasát písek z válečku. Druhý konec hadičky, vyvedený z válečku do říční vody, byl opatřen gumovou zátkou. Prvních 10 ml vody (objem hadičky) bylo před měřením vždy nasáto a vylito, aby byl systém zbaven vody, která v něm stála, a propláchnut. V dalších 5 ml vody nasáté z válečku byl přenosným membránovým oxymetrem (WTW Multi 3320) s automatickou teplotní korekcí změřen, bezprostředně po odběru, obsah rozpuštěného kyslíku. Měření obsahu kyslíku z intersticiální vody válečků bylo opakováno každých 14 dní, včetně měření teploty a obsahu kyslíku v říční vodě.
Obr. 3. Experimentální válečky (foto vlevo: I. Ibrahimovič)
Fig. 3. Experimental rollers (left photo: I. Ibrahimovič)
Při tvorbě těchto výzkumných válečků jsme se inspirovali od výzkumníků Capoulada a Pasca na konferenci v Bretani v roce 2014 [1]. Metoda jímání intersticiální vody z válečků za pomoci silikonové hadičky je podobná metodě použití minipiezometrů, kde je velmi žádoucí zavedení odběrového tělesa do podříčního dna hned na počátku výzkumu, aby nedocházelo ke kontaminaci vzorku intersticiální vody vodou povrchovou z důvodu opakovaného rozrušování sedimentů dna [12–16]. Ve své studii zaměřené na metodu měření kyslíku v říčních sedimentech za pomoci trubek z nerezové oceli, zavedených po celou dobu výzkumu do hyporheálu, autoři zjistili, že kontaminace zbytkovou vodou či zkreslení obsahu kyslíku v důsledku extrakce intersticiální vody pod tlakem jsou zanedbatelné [17].
Substrát
Substrátem pro vývoj biofilmu ve válcích v experimentálních krabicích i v experimentálních válečcích byl písek o velikosti 1–2 mm odebraný z Vltavy (obr. 4). Je to nejmenší možná frakce substrátu z hlediska velikosti ok síťoviny válečků a válců i z hlediska výzkumu množství jemného naplaveného organického materiálu (FPOM). Nejmenší možnou velikost zrn písku jsme zvolili i z důvodu největšího výskytu partikulovaného organického materiálu (POM) na zrnech sedimentu o frakci < 1 mm [18]. Dle Leichtfriedové [19] je hlavním důvodem osídlení této velikostní frakce zrn sedimentu větší plocha k osídlení pro mikrobiální společenstvo. Obdobná velikostní frakce je optimální pro chov juvenilních perlorodek [1]. Odebraný říční písek byl před použitím přesítován a vyžíhán pro sterilizaci.

Obr. 4. Odběr a zpracování písku o velikosti 1–2 mm z lokality Ovesná, který je následně inkubován ve válcích a válečcích
Fig. 4. Collection and processing of sand 1–2 mm in size from the Ovesná site, which is subsequently incubated in cylinders and rollers
Umístění
Na Dobré na Šumavě, Ovesné i Studené Vltavě zůstaly z podzimu 2019 umístěny ve dně experimentální krabice, do nichž byly 23. dubna 2020 vsunuty stojany s nově připravenými válci s vyžíhaným pískem. Do tří míst ve vzdálenosti 5 cm od krabice bylo umístěno vodorovně 6 malých válečků s hadičkami, vždy po dvojici. Jeden váleček z dvojice byl umístěn do hloubky 20 cm (stejně jako nejnižší válec v krabici) a druhý do hloubky 10 cm (stejně jako nejvyšší válec v krabici) (obr. 6). Dvě dvojice válečků byly doplněny o kontinuální teploměry HOBO Pendant® Temperature/Light 64K Data Logger, které byly také zavedeny do hloubky 10 a 20 cm za pomoci hřebíku. Teplota byla snímána každou hodinu.
Kolem krabice byla dále vybrána tři místa pro umístění sady vždy tří kusů malých válečků s hadičkami a jednoho velkého válce z krabice do hloubky 3–5 cm (obr. 5).

Obr. 5. Příklad umísťování válečků, teploměrů a jednoho válce do hloubky 3–5 cm hyporheálu na lokalitách Ovesná a Studená Vltava (zleva)
Fig. 5. Example of placing rollers, thermometers and one cylinder to a depth of 3–5 cm in the hyporheal at the Ovesná and Studená Vltava sites (from left)
Obr. 6. Příklad umísťování válečků kolem experimentální krabice do hloubky 10 cm hyporheálu na lokalitě Studená Vltava (z válečků umístěných v hloubce 20 cm jsou již vidět jen hadičky)
Fig. 6. Example of placement of rollers around the experimental box to a depth of 10 cm of the hyporheal at the Studená Vltava site (only the tubes are visible from the hyporheal rollers placed at a depth of 20 cm)
Každé z míst bylo doplněno dvěma kontinuálními teploměry umístěnými u válečku a pod ním. Rozmístění krabice a okolních válců a válečků bylo na všech třech lokalitách stejné. Ze všech malých válečků byla každých 14 dní jímána intersticiální voda za pomoci metr dlouhé silikonové hadičky a měřen obsah rozpuštěného kyslíku. Všechny válečky i válce byly označeny cedulkami s čísly, charakteristickými pro každou z lokalit (obr. 7).
Celkově bylo na každou z lokalit umístěno 15 kusů malých válečků s hadičkami, 5 kusů velkých válců, deset HOBO teploměrů do dna a jeden HOBO teploměr do říční vody.
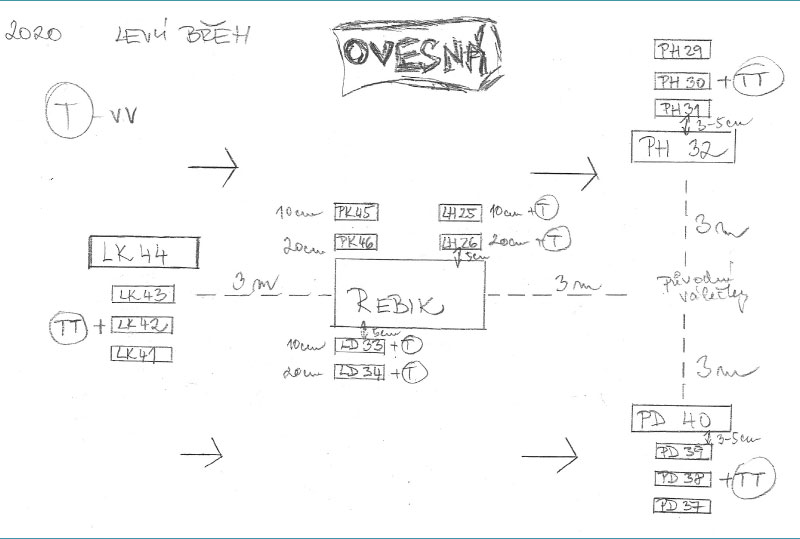
Obr. 7. Nákres umístění experimentálních zařízení v hyporheických sedimentech na jedné z lokalit – Ovesná. REBIK – experimentální krabice se dvěma válci v hloubce 10 a 20 cm, malé obdélníky znázorňují malé experimentální válečky a velké obdélníky velké experimentální válce, T – kontinuální teploměr
Fig. 7. Drawing of the location of experimental equipment in hyporheic sediments at one of the sites (Ovesná). REBIK – experimental box with two cylinders at a depth of 10 and 20 cm, small rectangles represent small experimental rollers and large rectangles large experimental cylinders, T – continuous thermometer
Vyjmutí
Veškeré válce, válečky i teploměry byly vyjmuty 5. listopadu 2020 a ihned proběhlo jejich zpracování. Ve velkých válcích byla v podmínkách in situ měřena respirace. Válce byly postupně napojeny na obvod s membránovým oxymet-rem (WTW Multi 3320) a čerpadlem, který simuloval proud vody prostupující hyporheickými sedimenty (sedimenty ve válci) (obr. 8). Celý oběh byl naplněn říční vodou z dané lokality. V průběhu měření bylo v 10minutových intervalech zaznamenáváno množství kyslíku v cirkulující vodě. Respirace biofilmu byla ve všech válcích měřena po stejný časový úsek (30 minut).
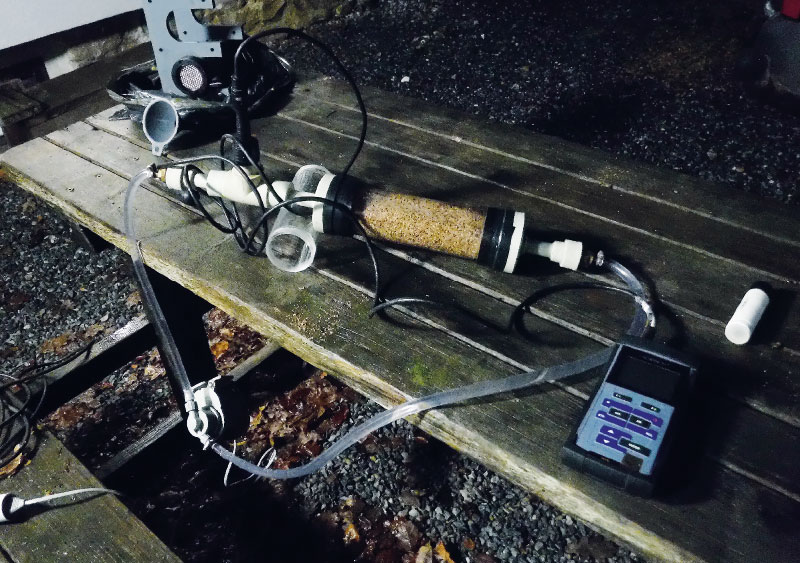

Obr. 8. Měření respirace ve válcích v podmínkách in situ
Fig. 8. Measurement of respiration in cylinders under in situ conditions
Z malých válečků byl vyplaven jemný organický materiál (frakce FPOM, tj. menší než 1 mm), dekantován a zamrazen (obr. 9). Válce z experimentálních krabic žádný detrit neobsahovaly. Následně byl substrát každého válce i válečku rozdělen na podvzorky, které byly zamrazeny.
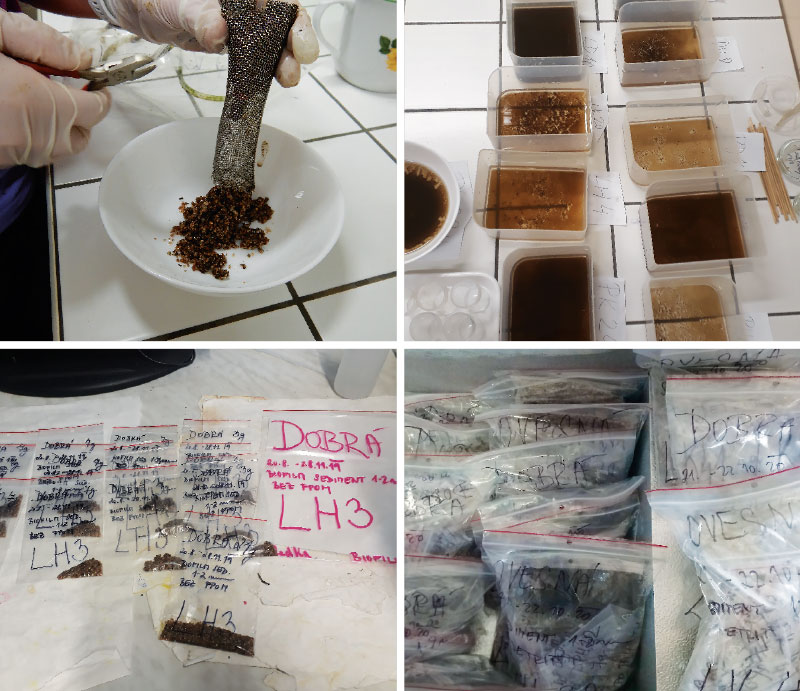

Obr. 9. Zpracování písku a jemného organického materiálu (FPOM) z vyjmutých válečků a válců v laboratoři (první foto: J. Horáčková)
Fig. 9. Processing of sand and fine organic material (FPOM) from removed rollers and cylinders in the laboratory (first photo: J. Horáčková)
Analýzy
Po vyjmutí experimentálních válců byla změřena respirace biofilmu in situ, která je jedním z indikátorů přítomnosti hyporheického biofilmu na inkubovaném sedimentu [20]. Bakteriální respirace (aerobní) organického uhlíku na anorganický je prostřednictvím změn v koncentraci kyslíku velmi dobře měřitelným procesem heterotrofního metabolismu. [8, 10].
Jako hlavní proxy parametry vývoje hyporheických biofilmů na inkubovaných sedimentech jsme zvolili stanovení koncentrace polysacharidů dle Duboise a dále celkové množství organické hmoty na zrnech sedimentu a v FPOM, vyjadřované jako celkový organický uhlík (TOC) [21]. Obě analýzy byly provedeny na Přírodovědecké fakultě UP v Olomouci studentkou Magdalenou Firlovou pod dohledem doc. Martina Rulíka.
Stanovení celkového množství organické hmoty v biofilmu bylo provedeno metodou ztráty žíháním (loss of ignition, LOI) dle [22]. Podstatou metody je sušení inkubovaného sedimentu či FPOM 24 hodin při 100 °C v sušárně a jeho následné vyžíhání v peci po dobu 3 hodin při teplotě 550 °C. Během procesu je zaznamenáván hmotnostní rozdíl sedimentu či FPOM po vysušení a následně po vyžíhání. Získané hodnoty organické hmoty byly následně přepočteny na hodnoty TOC vynásobením koeficientem 0,45.
Stanovení koncentrace polysacharidů dle Duboise je popsáno jako metoda dehydratace cukrů ve vzorku za pomoci kyseliny sírové, následné kondenzace furfuralů a vzniku barevných produktů s fenolem, které lze stanovit za pomoci spektrofotometru [23, 24].
Ke statistickému vyhodnocení dat byl použit software R. Vztahy mezi jednotlivými parametry hyporheického biofilmu byly ověřovány graficky a lineární regresí.
VÝSLEDKY
Měření kyslíku v intersticiální vodě
Nasycení intersticiální vody válečků kyslíkem (obr. 10–12) vykazovalo na jednotlivých lokalitách během roku 2020 velmi podobné hodnoty i trend. Koncentrace kyslíku v intersticiální vodě válečků přesahovala po většinu zkoumaného období hodnotu 65 % (jedná se o nejnižší možný obsah kyslíku ve vodě tolerovaný perlorodkou říční), výjimkou bylo letní období, kdy došlo na všech lokalitách k nápadnému poklesu nasycení pod tuto hraniční hodnotu.
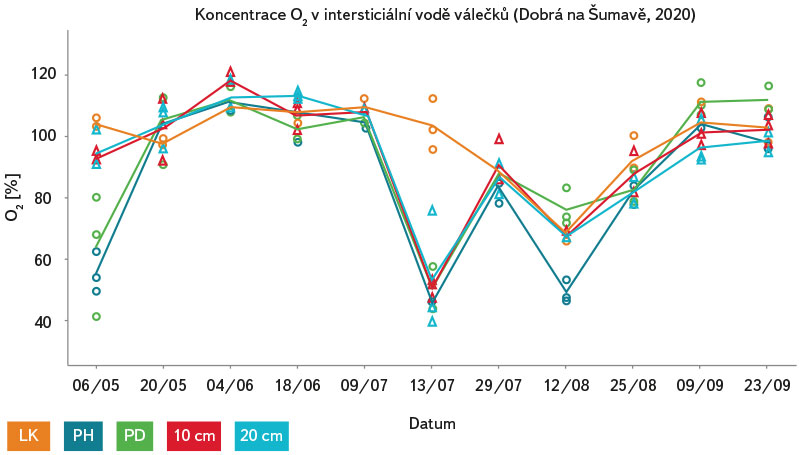
Obr. 10. Průměrné hodnoty nasycení intersticiální vody kyslíkem (%) ve třech experimentálních válečcích na každém z 5 míst (LK, PH, PD 3–5 cm pod povrchem) ve vodním toku v období 6. května až 23. září 2020 na lokalitě Dobrá na Šumavě
Fig. 10. Average values of oxygen saturation in interstitial water (%) of three experimental rollers at each of 5 sites (LK, PH, PD 3–5 cm below the surface) in the stream during the period 6 May – 23 September 2020 at the Dobrá site in Šumava
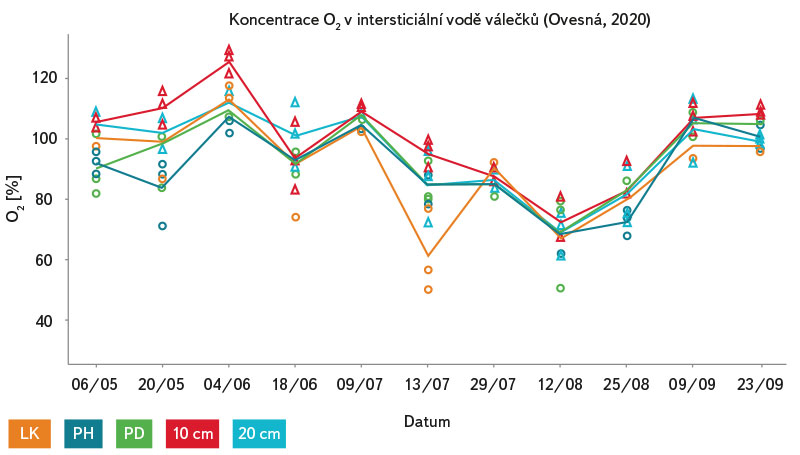
Obr. 11. Průměrné hodnoty nasycení intersticiální vody kyslíkem (%) ve třech experimentálních válečcích na každém z 5 míst (LK, PH, PD 3–5 cm pod povrchem) v toku v období 6. května až 23. září 2020 na lokalitě Ovesná
Fig. 11. Average values of oxygen saturation in the interstitial water (%) of three experimental rollers at each of the 5 sites (LK, PH, PD 3–5 cm below the surface) in the stream during the period 6 May – 23 September 2020 at the Ovesná site
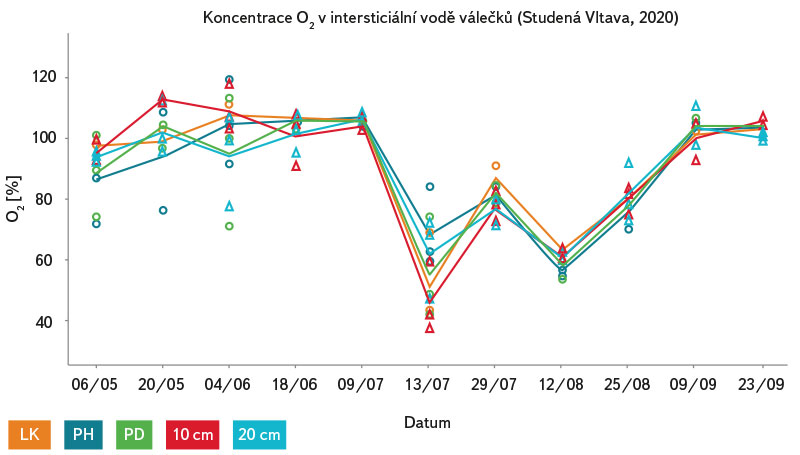
Obr. 12. Průměrné hodnoty nasycení intersticiální vody kyslíkem (%) ve třech experimentálních válečcích na každém z 5 míst (LK, PH, PD 3–5 cm pod povrchem) v toku v období 6. května až 23. září 2020 na lokalitě Studená Vltava
Fig. 12. Average values of oxygen saturation in interstitial water (%) of three experimental rollers at each of 5 sites (LK, PH, PD 3–5 cm below the surface) in the stream during the period 6 May – 23 September 2020 at the Studená Vltava site
Teplota vody
Na obr. 13 je znázorněn záznam měření teploty za pomocí kontinuálních teploměrů HOBO Pendant®, které byly umístěny v hyporheálu spolu s válečky v hloubkách 3, 10 a 20 cm. Jeden teploměr byl umístěn do volné říční vody. Zároveň byla každých 14 dní při měření koncentrace kyslíku v intersticiální vodě válečků klasickým digitálním teploměrem měřena i teplota intersticiální vody jímané stříkačkami. V grafu je viditelný shodný průběh teplot měřených ve stejné dny sezony, avšak odlišnými přístroji. Teploty naměřené ve stříkačkou odebrané intersticiální vodě válečků se od teplot naměřených kontinuálními teploměry zavedenými v hyporheálu lišily až o zhruba 2 stupně. Na obr. 14 je znázorněn velmi podobný průběh teplot snímaných všemi kontinuálními teploměry na třech výzkumných lokalitách (Dobrá na Šumavě, Ovesná a Studená Vltava). Nejteplejší lokalitou byla Ovesná, nejstudenější Studená Vltava.
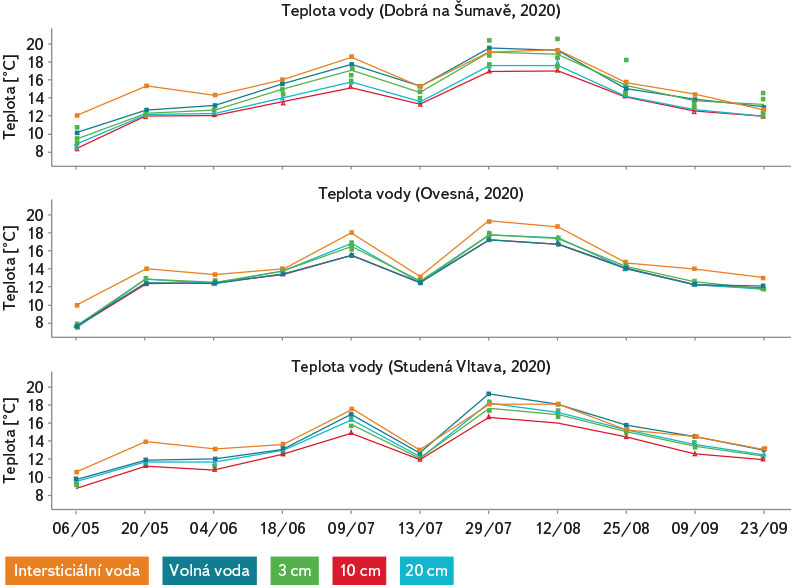
Obr. 13. Teplota intersticiální vody měřená za pomoci kontinuálních teploměrů HOBO Pendant® umístěných v hyporheických sedimentech spolu s experimentálními válečky v hloubkách 3, 10 a 20 cm v porovnání s teplotou („intersticiální voda“), která byla měřena klasickým digitálním teploměrem v intersticiální vodě malých válečků při každém měření koncentrace kyslíku, tj. od 6. května do 23. září 2020 na třech lokalitách Vltavy (Dobrá na Šumavě, Ovesná, Studená Vltava) a její porovnání s teplotou volné říční vody měřené kontinuálním teploměrem HOBO Pendant®
Fig. 13. Interstitial water temperature measured using HOBO Pendant® continuous thermometers placed in hyporheic sediments together with experimental rollers at depths of 3, 10 and 20 cm compared to the temperature („interstitial water“) measured with a conventional digital thermometer in the interstitial water of small rollers at each oxygen concentration measurement, i. e. 6 May – 23 September 2020 at three sites on the Vltava (Dobrá na Šumavě, Ovesná, Studená Vltava) and compared with the temperature of free river water measured with the HOBO Pendant® thermometer
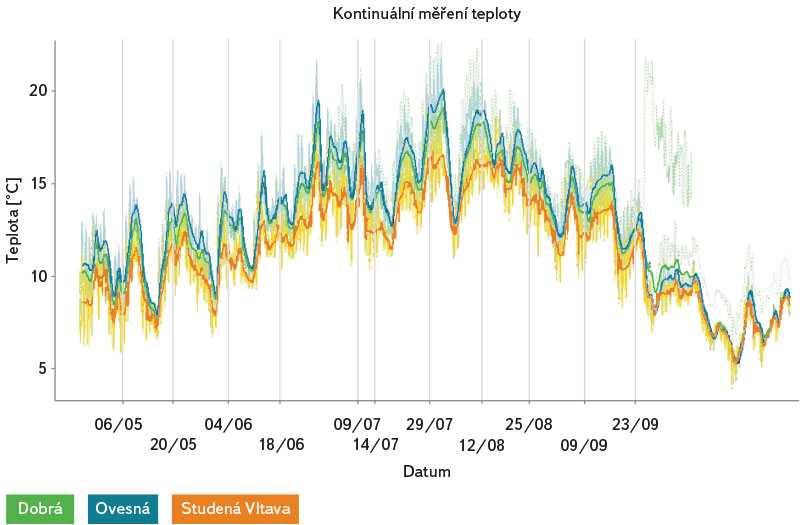
Obr. 14. Teplota intersticiální vody měřená od 6. května do 23. září 2020 na třech lokalitách (Dobrá na Šumavě, Ovesná a Studená Vltava) za pomoci kontinuálních teploměrů HOBO Pendant® umístěných ve volné říční vodě a v hyporheálu v hloubkách 3, 10 a 20 cm
Fig. 14. Interstitial water temperature measured from 6 May to 23 September 2020 at three sites (Dobrá na Šumavě, Ovesná and Studená Vltava) using HOBO Pendant® continuous thermometers placed in free river water and hyporheal at depths of 3, 10 and 20 cm
Respirace
Měření respirace in situ ve válcích z experimentálních krabic poukázalo – prostřednictvím měření změn obsahu kyslíku po dobu 30 minut v každém z válců – na přítomnost životaschopného mikrobiálního společenstva (obr. 15). U válců volně exponovaných v hyporheickém sedimentu 3–5 cm pod povrchem byly však při měření v intervalu 30 minut zaznamenány mnohem větší změny v koncentraci kyslíku v každém z válců (obr. 16). To naznačuje mnohem větší biomasu mikrobiálního společenstva, respektive vyšší aktivitu, než na sedimentu válců exponovaných v krabicích.
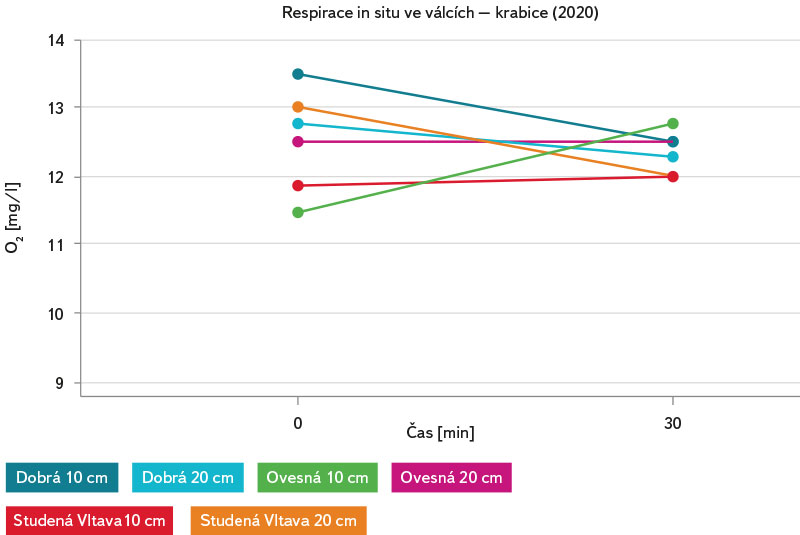
Obr. 15. Respirace in situ ve válcích z experimentálních krabic exponovaných na třech lokalitách (Dobrá na Šumavě, Ovesná a Studená Vltava) od jara do podzimu 2020
Fig. 15. In situ respiration in cylinders from experimental boxes exposed at three sites (Dobrá na Šumavě, Ovesná and Studená Vltava) from spring to autumn 2020
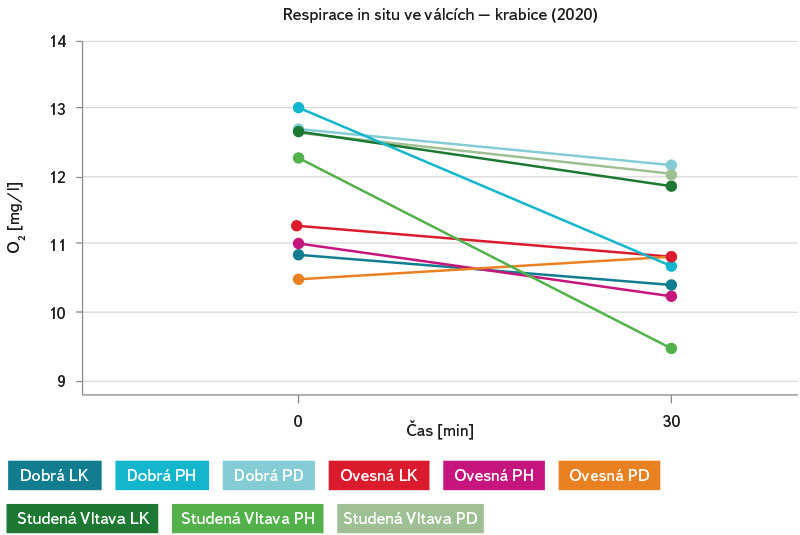
Obr. 16. Respirace in situ ve válcích exponovaných na třech místech kolem krabice v hloubce 3–5 cm spolu s malými válečky na lokalitách Dobrá na Šumavě, Ovesná a Studená Vltava
Fig. 16. Respiration in situ in cylinders exposed in three places around the box at a depth of 3–5 cm together with small rollers at the sites Dobrá na Šumavě, Ovesná and Studená Vltava
Koncentrace polysacharidů
V inkubovaných hyporheických sedimentech byl Duboisovou metodou stanoven obsah polysacharidů, které tvoří hlavní stavební prvek biofilmů a nacházejí se v extracelulární polymerní matrici (EPM). Touto matricí jsou jednotlivé buňky biofilmu obaleny a předpokládáme, že je produkována bakteriemi jako ochranná a propojující vrstva celého mikrobiálního společenstva – biofilmu [10].
Na obr. 17 vidíme, že nejnižší hodnoty koncentrace polysacharidů byly na lokalitách Dobrá na Šumavě a Studená Vltava naměřeny u válců, jež byly inkubovány v krabici v hloubkách sedimentů 10 a 20 cm. Zajímavé je pozorování hodnot koncentrace polysacharidů u válečků umístěných volně v hyporheickém prostředí v blízkém sousedství krabice v hloubce 10 cm. U lokality Ovesná můžeme vidět, že u těchto válečků byly analyzovány vyšší koncentrace polysacharidů než u válečků umístěných těsně pod povrchem dna (hloubka 3–5 cm). Na základě této koncentrace polysacharidů lze předpokládat u válečků inkubovaných v hloubkách 10 a 20 cm kolem krabice i větší množství celkového organického uhlíku (TOC). Nejvyšší koncentrace polysacharidů v biofilmu byly obecně naměřeny na lokalitě Ovesná (obr. 18).
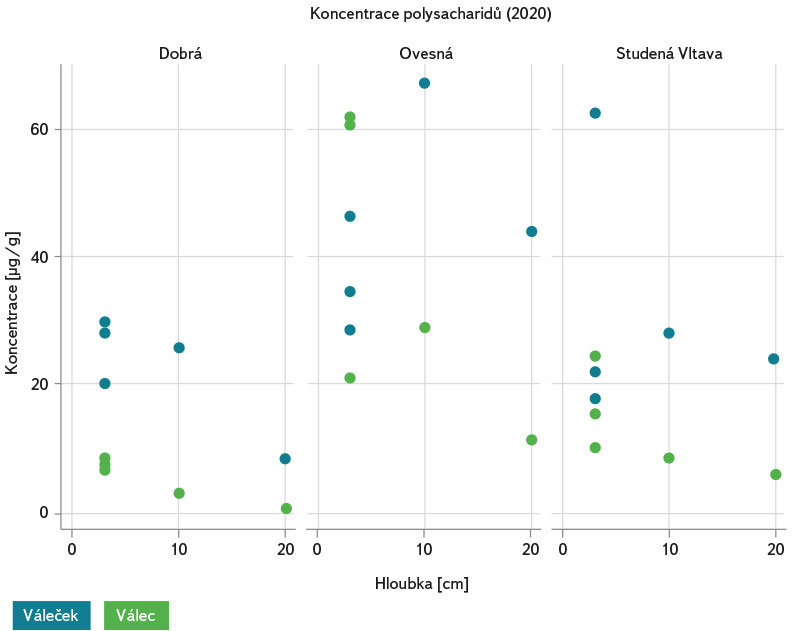
Obr. 17. Koncentrace polysacharidů v biofilmu na písku o velikosti zrn 1–2 mm, inkubovaného ve válečcích a válcích v hloubce 3–5 cm pod povrchem hyporheálu, válečcích v hloubkách 10 a 20 cm pod povrchem hyporheálu a ve válcích umístěných v krabici v hloubkách 10 a 20 cm na třech lokalitách (Dobrá na Šumavě, Ovesná a Studená Vltava) od jara do podzimu 2020
Fig. 17. Concentration of biofilm polysaccharides on sand with grain size 1–2 mm incubated in rollers and cylinders at depths of 3–5 cm below the hyporheal surface, rollers at depths of 10 and 20 cm below the hyporheal surface and cylinders placed in a box at depths of 10 and 20 cm at three sites (Dobrá na Šumavě, Ovesná and Studená Vltava) from spring to autumn 2020
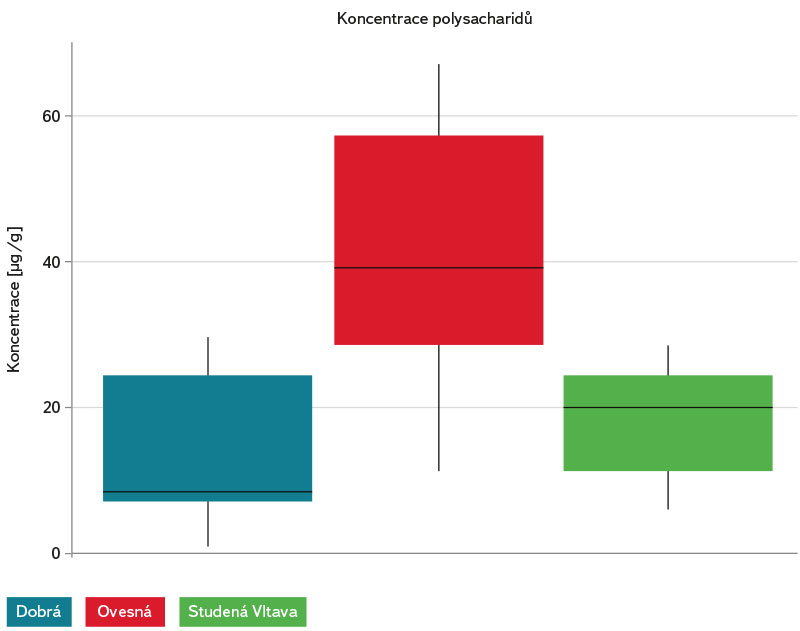
Obr. 18. Koncentrace polysacharidů v biofilmu na písku o velikosti zrn 1–2 mm, stanovená ze všech experimentálních zařízení, která byla na dané lokalitě umístěna od jara do podzimu 2020 – porovnání všech tří lokalit
Fig. 18. Concentration of polysaccharides in biofilm on sand with grain size 1–2 mm, determined from all experimental devices deployed at a given site from spring to autumn 2020 – comparison of all three sites
Stanovení celkového organického uhlíku na sedimentu
Nejvyšší hodnoty procentuálního zastoupení celkového organického uhlíku (TOC) byly zjištěny ve válcích exponovaných v hyporheické zóně v hloubce 3–5 cm pod povrchem na lokalitě Ovesná (obr. 19). Zajímavým zjištěním jsou velmi podobné hodnoty TOC ve válcích a válečcích umístěných volně v hyporheických sedimentech a ve válcích, které byly po celou dobu výzkumu exponovány v krabici na všech třech zkoumaných lokalitách (Dobrá na Šumavě, Ovesná a Studená Vltava). Dle obr. 20 byla nejvyššími hodnotami TOC (ze všech experimentálních zařízení dohromady) charakteristická lokalita Ovesná.
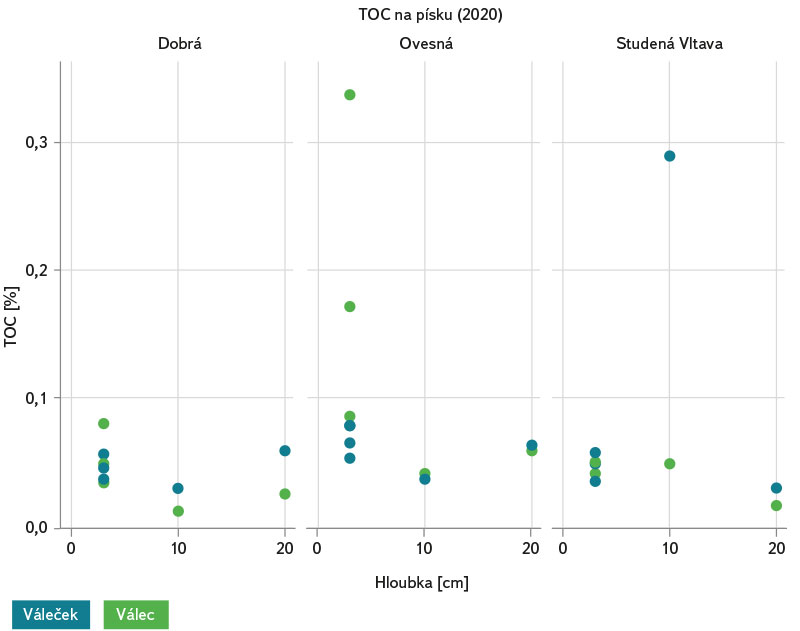
Obr. 19. Procentuální zastoupení celkového organického uhlíku (TOC) na písku o velikosti zrn 1–2 mm, inkubovaného ve válečcích a válcích v hloubce 3–5 cm pod povrchem hyporheálu, válečcích v hloubkách 10 a 20 cm pod povrchem hyporheálu a ve válcích umístěných v krabici v hloubkách 10 a 20 cm na třech lokalitách (Dobrá na Šumavě, Ovesná a Studená Vltava) od jara do podzimu 2020
Fig. 19. Percentual share of total organic carbon (TOC) in sand with grain size 1–2 mm incubated in rollers and cylinders at depths of 3–5 cm below the hyporheal surface, rollers at depths of 10 and 20 cm below the hyporheal surface and cylinders placed in a box at depths of 10 and 20 cm at three sites (Dobrá na Šumavě, Ovesná and Studená Vltava) from spring to autumn 2020
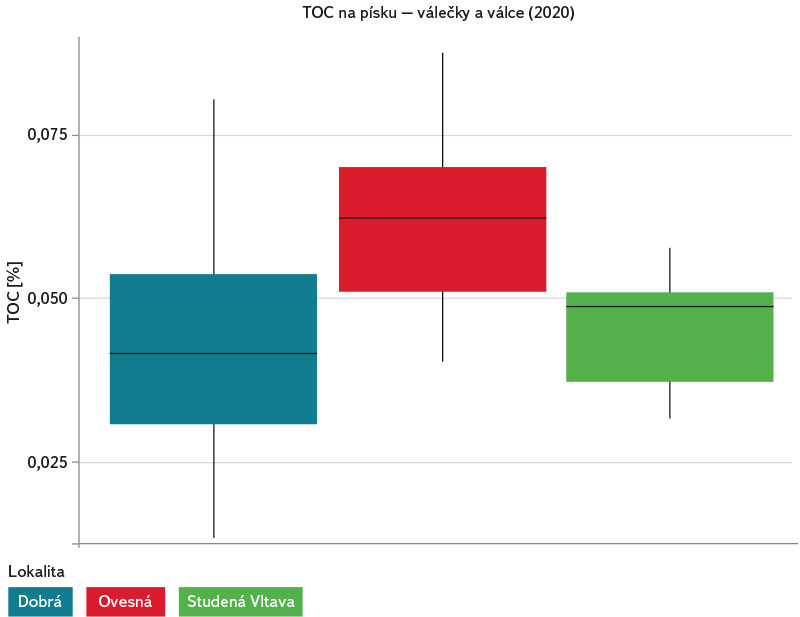
Obr. 20. Procentuální zastoupení celkového organického uhlíku (TOC) na písku o velikosti zrn 1–2 mm, stanovené ze všech experimentálních zařízení, která byla na dané lokalitě umístěna od jara do podzimu 2020 – porovnání všech tří lokalit
Fig. 20. Percentual share of total organic carbon (TOC) in sand with grain size 1–2 mm, determined from all experimental devices deployed at the site from spring to autumn 2020 – comparison of all three sites
Vztahy mezi parametry
Při zkoumání vztahů mezi jednotlivými sledovanými parametry je vidět slabý přímý lineární vztah mezi množstvím TOC (%) na sedimentech a koncentrací polysacharidů v biofilmu (obr. 21). Mezi množstvím TOC a nasycením intersticiální vody kyslíkem nebyl zjištěn žádný statisticky signifikantní vztah (obr. 22).
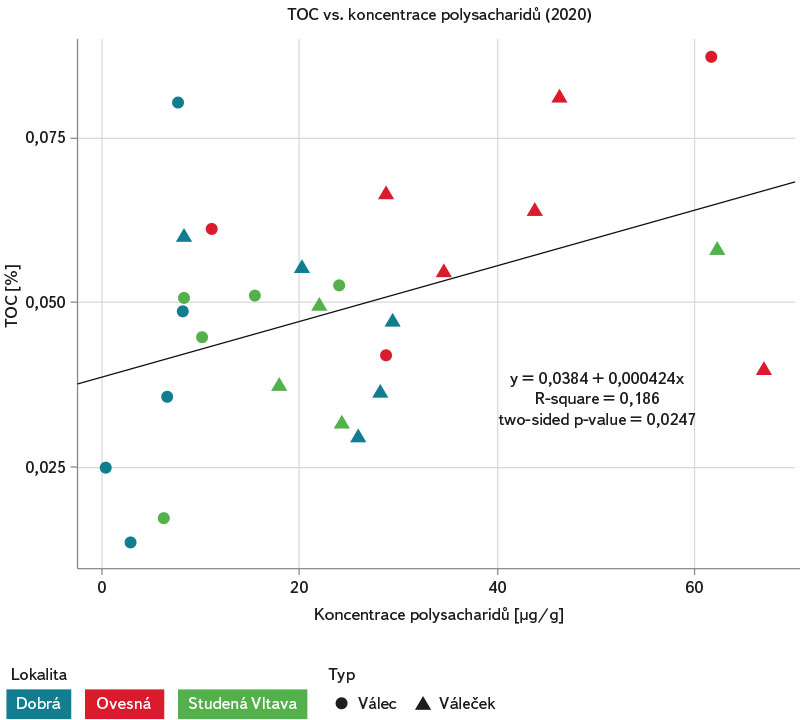
Obr. 21. Vztah mezi množstvím celkového organického uhlíku (TOC %) a koncentrací polysacharidů v biofilmu válečků a válců z lokalit Dobrá na Šumavě, Ovesná a Studená Vltava, 2020
Fig. 21. Relationship between the amount of total organic carbon (TOC %) and the concentration of polysaccharides in the biofilm of rollers and cylinders from the sites Dobrá na Šumavě, Ovesná and Studená Vltava, 2020
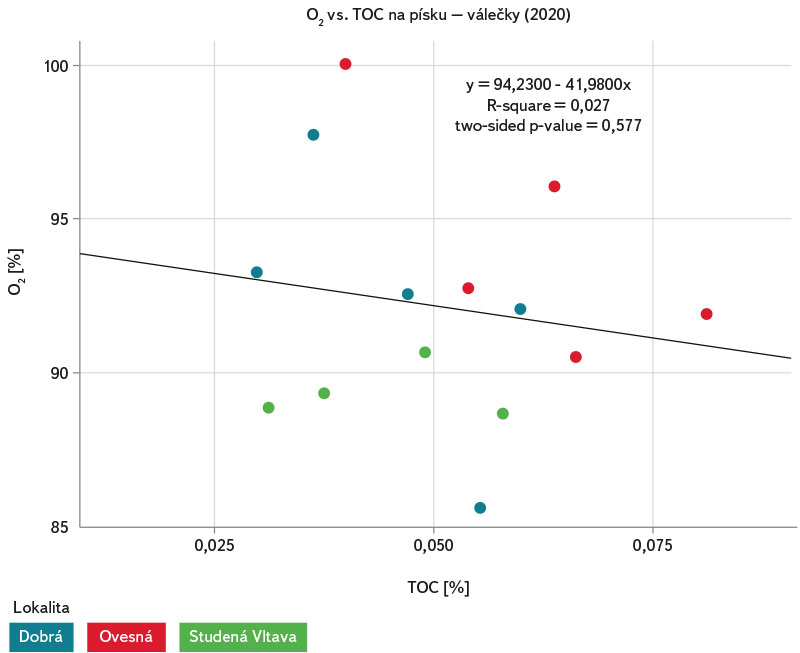
Obr. 22. Vztah mezi množstvím celkového organického uhlíku (TOC %) a nasycením intersticiální vody válečků kyslíkem z lokalit Dobrá na Šumavě, Ovesná a Studená Vltava, 2020
Fig. 22. Relationship between total organic carbon (TOC %) and oxygen saturation in the interstitial water of rollers from the sites Dobrá na Šumavě, Ovesná and Studená Vltava, 2020
ZÁVĚR
Detekce polysacharidů jakožto proxy pro přítomnost biofilmu na inkubovaném sedimentu v experimentálních válcích a válečcích naznačuje, že intersticiální sediment byl v průběhu roku v různé míře kolonizován mikrobiálním biofilmem. Tento závěr podporují i výsledky z měření respirace in situ ve velkých válcích uložených v experimentálních krabicích i mimo ně. Kromě vlastního biofilmu se na zrnech písku nachází adherovaný organický materiál, který společně s vlastním biofilmem zahrnujeme pod označení TOC – tj. celkový organický uhlík. Nejvyšší hodnoty procentuálního podílu TOC i koncentrace polysacharidů byly zjištěny na sedimentech inkubovaných na lokalitě Ovesná, která leží pod soutokem Teplé a Studené Vltavy a je charakterizována obecně vyšší koncentrací živin a nejvyšší průměrnou teplotou intersticiální vody.
Mezi množstvím organického uhlíku (TOC %), polysacharidů na inkubovaných sedimentech a kyslíkem rozpuštěným v intersticiální vodě nebyl prokázán žádný vztah. Fluktuace obsahu kyslíku v intersticiální vodě v okolí inkubovaného sedimentu ve válečcích je ovlivněna spíše kolmatací sedimentů jemným organickým materiálem, nikoli rostoucí biomasou a respirací mikrobiálního společenstva (biofilmu). Koncentrace kyslíku v intersticiální vodě válečků přesahovala po většinu zkoumaného období hodnotu 65 % (jedná se o nejnižší možný obsah kyslíku ve vodě tolerovaný perlorodkou říční [25]), výjimkou bylo letní období, kdy byly naměřeny hodnoty nižší. Důvody tohoto náhlého poklesu obsahu kyslíku na všech studovaných lokalitách však zatím nejsme schopni exaktně vysvětlit, příčinou by mohlo být prudké zvýšení průtoků v důsledku letních bouřek spojené s erozí půdy a následnou kolmatací dna organickým materiálem.
Výzkum hyporheických biofilmů v NP Šumava pokračuje i v letošním roce (2021). Současně s tímto výzkumem probíhají ještě některé další analýzy vzorků z roku 2020, např. stanovení poměru C : N ve vzorcích FPOM, zachyceného v experimentálních válcích a válečcích, který nám poskytuje informaci o dostupnosti a kvalitě hyporheických biofilmů jakožto možné potravy pro juvenilní perlorodky.
Poděkování
Příspěvek vznikl za podpory projektu „Posílení a ochrana populace perlorodky říční v NP Šumava: část 1 – Odchov, část 2 – Analýzy“ (NPS 04613/2017) a dvou interních grantů „Výzkum hyporheických biofilmů Vltavy v NP Šumava s ohledem na juvenilní perlorodky, jejich potravní nároky a dostatečné nasycení intersticiální vody kyslíkem“ (1645, 3600.52.11/2020) financovaných z prostředků na podporu rozvoje VÚV TGM. Děkuji též Vojtěchu Mrázkovi za technickou pomoc po celou dobu výzkumu.
Příspěvek prošel lektorským řízením.